List of Papers and Blog posts
Controlling conditional language models without catastrophic forgetting
Tomasz Korbak, Hady Elsahar, German Kruszewski, Marc Dymetman
International Conference on Machine Learning, ICML2022 [paper] [slides] [code]
In this work we target an the important question of how to adapt pre-trained generative models to meet human requirements without destroying their general capabilities ("catastrophic forgetting"). Recent work has proposed to solve this problem by representing task-specific requirements through energy-based models (EBMs) and approximating these EBMs using distributional policy gradients (DPG). Despite its effectiveness, this approach is however limited to unconditional distributions. In this paper, we extend DPG to conditional tasks by proposing Conditional DPG (CDPG). We evaluate CDPG on four different control objectives across three tasks (translation, summarization and code generation) and two pretrained models (T5 and GPT-Neo). Our results show that fine-tuning using CDPG robustly moves these pretrained models closer towards meeting control objectives and — in contrast with baseline approaches — does not result in catastrophic forgetting.
Controlling Conditional Language Models with Distributional Policy Gradients
CtrlGen workshop Neurips 2021 [paper]
Tomasz Korbak, Hady Elsahar, German Kruszewski, Marc Dymetman
Machine learning is shifting towards general-purpose pretrained generative models. However, due to their generic training methodology, these models often fail to meet some of the downstream requirements (e.g. hallucination in abstractive summarization or wrong format in automatic code generation). This raises an important question on how to adapt pre-trained generative models to a new task without destroying its capabilities. Recent work has suggested to solve this problem by representing task-specific requirements through energy-based models (EBMs) and approximating these EBMs using distributional policy gradients (DPG). In this paper, we extend this approach to conditional tasks by proposing Conditional DPG (CDPG). We evaluate CDPG on three different control objectives across two tasks: summarization with T5 and code generation with GPT-Neo.
Sampling from Discrete Energy-Based Models with Quality/Efficiency Trade-offs
CtrlGen workshop Neurips 2021 [paper]
Bryan Eikema, Germán Kruszewski, Hady Elsahar, Marc Dymetman
A new approximate sampling technique, Quasi Rejection Sampling (QRS), that allows for a trade-off between sampling efficiency and sampling quality, while providing explicit convergence bounds and diagnostics. QRS capitalizes on the availability of high-quality global proposal distributions obtained from deep learning models. We demonstrate the effectiveness of QRS sampling for discrete EBMs over text for the tasks of controlled text generation with distributional constraints and paraphrase generation. We show that we can sample from such EBMs with arbitrary precision at the cost of sampling efficiency.
Energy-Based Models for Code Generation under Compilability Constraints
NLP4prog at ACL2021. [Paper]
Tomasz Korbak, Hady Elsahar, Marc Dymetman, German Kruszewski
In this work, We define an Energy-Based Model (EBM) representing a pre-trained generative model with an imposed constraint of generating only compilable sequences of programming languages. Our proposed approach is able to improve compilability rates without sacrificing the diversity and complexity of the generated samples.
A Distributional Approach To Controlled Text Generation
ICLR2021 ( Oral presentation - top 2.1% )
Muhammad Khalifa* Hady Elsahar* Marc Dymetman*
* first author equal contribution
[Paper] [code] [Blogpost] [Twitter Thread]
We propose a novel approach to Controlled Text Generation, relying on Constraints over Distributions, Information Geometry, and Sampling from Energy-Based Models.
Participatory Research for Low-resourced Machine Translation: A Case Study in African Languages
(∀ ∗ et al.) EMNLP 2020 Findings
[Paper] [Code] [summary]
Research in NLP lacks geographic diversity, and the question of how NLP can be scaled to low-resourced languages has not yet been adequately solved. ‘Low-resourced’-ness is a complex problem going beyond data availability and reflects systemic problems in society. In this paper, we focus on the task of Machine Translation (MT), that plays a crucial role for information accessibility and communication worldwide. Despite immense improvements in MT over the past decade, MT is centered around a few high-resourced languages. As MT researchers cannot solve the problem of low-resourcedness alone, we propose participatory research as a means to involve all necessary agents required in the MT development process. We demonstrate the feasibility and scalability of participatory research with a case study on MT for African languages.
Its implementation leads to a collection of novel translation datasets, MT benchmarks for over 30 languages, with human evaluations for a third of them, and enables participants without formal training to make a unique scientific contribution. Benchmarks, models, data, code, and evaluation results are released at https://github.com/masakhane-io/masakhane-mt.
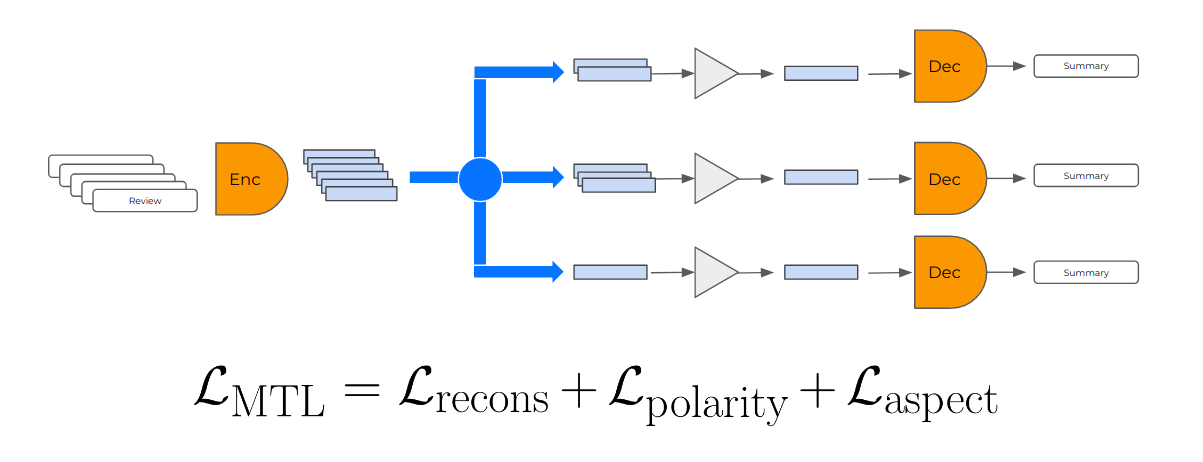
Self-Supervised and Controlled Multi-Document Opinion Summarization
Hady Elsahar, Maxmin Coavoux, Matthias Gallé, Jos Rozen
EACL2021 [Paper] [Twitter summary]
We address the problem of unsupervised abstractive summarization of collections of user generated reviews with self-supervision and control. We propose a self-supervised setup that considers an individual document as a target summary for a set of similar documents. This setting makes training simpler than previous approaches by relying only on standard log-likelihood loss. We address the problem of hallucinations through the use of control codes, to steer the generation towards more coherent and relevant summaries.Finally, we extend the Transformer architecture to allow for multiple reviews as input.
Unsupervised Aspect-Based Abstractive Summarization
User-generated reviews of products or services provide valuable information to customers. However, it is often impossible to read each of the potentially thousands of reviews: it would therefore save valuable time to provide short summaries of their contents. We address opinion summarization, a multi-document summarization task, with an unsupervised abstractive summarization neural system. Our system is based on (i) a language model that is meant to encode reviews to a vector space, and to generate fluent sentences from the same vector space (ii) a clustering step that groups together reviews about the same aspects and allows the system to generate summary sentences focused on these aspects. Our experiments on the Oposum dataset empirically show the importance of the clustering step…
Maxmin Caovoux, Hady Elsahar, Matthias Galle
NEWSUM@EMNLP 2019 [Paper]
To Annotate or Not? Predicting Performance Drop under Domain Shift
Hady Elsahar, Matthias Galle
NAVER LABS Europe
EMNLP 2019
In this paper, we propose a method that can predict the drop inaccuracy of a model suffering domain-shift with an error rate as little as 2.15% for sentiment analysis and 0.89% for POS tagging
respectively, without needing any labelled examples from the target domain.
Zero-Shot Question Generation from Knowledge Graphs for Unseen Predicates and Entity Types
Hady Elsahar, Christophe Gravier, Frederique Laforest
NAACL2018
We present a neural model for question generation from knowledge graphs triples in a “Zero-shot” setup, that is generating questions for predicate, subject types or object types that were not seen at training time. Our model leverages triples occurrences in the natural language corpus in a encoder-decoder architecture, paired with an original part-of-speech copy action mechanism to generate questions. Benchmark and human evaluation show that our model outperforms state-of-the-art on this task.
[code]
Mind the (Language) Gap: Generation of Multilingual Wikipedia Summaries from Wikidata for ArticlePlaceholders
Lucie-Aimée Kaffee * , Hady Elsahar * , Pavlos Vougiouklis* et al. (* first author equal contrib.)
ESWC2018
We focus on an important support for such summaries: ArticlePlaceholders, a dynamically generated content pages in underserved Wikipedias. They enable native speakers to access existing information in Wikidata. To extend those ArticlePlaceholders, we provide a system, which processes the triples of the KB as they are provided by the ArticlePlaceholder, and generate a comprehensible textual summary. This datadriven approach is employed with the goal of understanding how well it matches the communities’ needs on two underserved languages on the Web: Arabic, a language with a big community with disproportionate access to knowledge online, and Esperanto, an easily-acquainted, artificial language whose Wikipedia content is maintained by a small but devoted community.
[Code]
Learning to Generate Wikipedia Summaries for Underserved Languages from Wikidata
Lucie-Aimée Kaffee * , Hady Elsahar * , Pavlos Vougiouklis* et al. (* first author equal contrib.)
NAACL2018
In this work, we investigate the generation of open domain Wikipedia summaries in underserved languages using structured data from Wikidata. To this end, we propose a neural network architecture equipped with copy actions that learns to generate single-sentence and comprehensible textual summaries from Wikidata triples.
[Code]
Neural Wikipedian: Generating Textual Summaries from Knowledge Base Triples
Pavlos Vougiouklis , Hady Elsahar , Lucie-Aimee Kaffee, et al.
Journal of Web Semantics 2018
We propose an end-to-end trainable system that is able to generate a textual summary given a set of triples as input. The generated summary discusses various aspects of the information encoded within the input triple set. Our approach does not require any hand-engineered templates and can be applied to a great variety of domains. We propose an method of building a loosely aligned dataset of DBpedia and Wikidata triples with Wikipedia summaries in order to satisfy the training requirements of our system. Using these datasets, we have demonstrated that our technique is capable of scaling to domains with vocabularies of over 400k words.
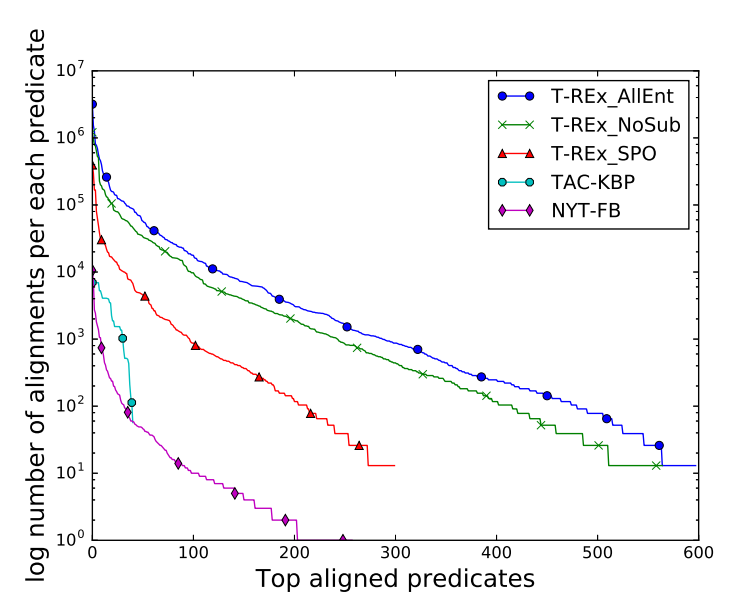
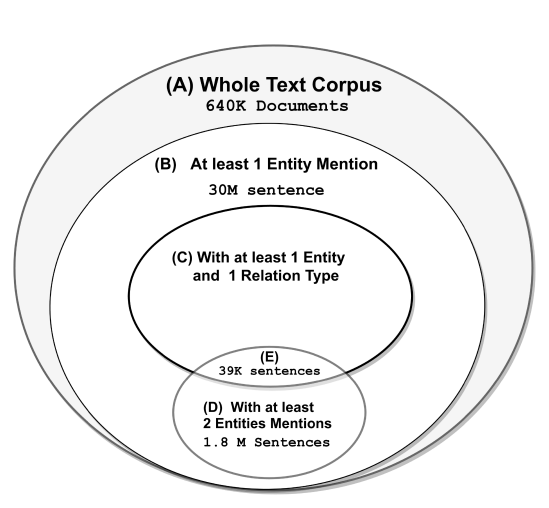
T-REx: A Large Scale Alignment of Natural Language with Knowledge Base Triples
Hady Elsahar, Pavlos Vougiouklis, Arslen Remaci, et al.
LREC2018
In this paper we present T-REx, a dataset of large scale alignments between Wikipedia abstracts and Wikidata triples. T-REx consists of 11 million triples aligned with 3.09 million Wikipedia abstracts (6.2 million sentences). T-REx is two orders of magnitude larger than the largest available alignments dataset and covers 2.5 times more predicates. Additionally, we stress the quality of this language resource thanks to an extensive crowdsourcing evaluation.
[Code] [T-REx Dataset]
High Recall Open IE for Relation Discovery
Hady Elsahar, Christophe Gravier, Frederique Laforest
IJCNLP 2017
Relation Discovery discovers predicates (relation types) from a text corpus relying on the co-occurrence of two named entities in the same sentence. This is a very narrowing constraint: it represents only a small fraction of all relation mentions in practice. In this paper we propose a high recall approach for Open IE, which enables covering up to 16 times more sentences in a large corpus. Comparison against OpenIE systems shows that our proposed approach achieves 28% improvement over the highest recall OpenIE system and 6% improvement in precision than the same system.
Building Large Arabic Multi-domain Resources for Sentiment Analysis
Hady Elsahar, Samhaa R. El-Beltagy
CICLing2015 [Best Paper Award]
While there has been a recent progress in the area of Arabic Sentiment Analysis, most of the resources in this area are either of limited size, domain specific or not publicly available. In this paper, we address this problem by generating large multi-domain datasets for Sentiment Analysis in Arabic. The datasets were scrapped from different reviewing websites and consist of a total of 33K annotated reviews for movies, hotels, restaurants and products. Moreover we build multi-domain lexicons from the generated datasets. Different experiments have been carried out to validate the usefulness of the datasets and the generated lexicons for the task of sentiment classification. From the experimental results, we highlight some useful insights addressing: the best performing classifiers and feature representation methods, the effect of introducing lexicon based features and factors affecting the accuracy of sentiment classification in general. All the datasets, experiments code and results have been made publicly available for scientific purposes.
[Code & Datasets]